There is a plane that is taking off and it is that of the fourth industrial revolution. Industry 4.0 is not only the introduction of a new technology but it is a radical cultural change, based on technologies with the potential to transform companies.
If the old revolutions were driven by innovations in production processes and systems, now new opportunities for companies come in the form of disruptive innovations in a smart, interconnected and innovative context.
Those who stay behind will no longer be competitive, which is why it is important to secure your ticket on board.
Whatis Industry 4.0
The concept of Industry 4.0 is associated with the phenomenon of the fourth industrial revolution and represents an important opportunity for companies. Industry 4.0 introduces intelligent machines into the production system, interconnected to each other and to the internet, and new smart factories are characterised by digitised production, fluid processes and modern production systems.
The use of key enabling technologies (KETs) promises to introduce new life into the production system, connecting all company assets and allowing the company to benefit from greater productivity and less waste. From an increasingly disruptive digital transformation, new technological and cultural paradigms emerge that involve the manufacturing system in all its forms.
The term “industry 4.0” was coined in Germany, more precisely at the Hanover Fair in 2011, as part of the project that started a working group that presented the German federal government with a plan for the implementation of Industry 4.0 based on long-term policies for the digitalization of the manufacturing sector.
Different Types of Industry
Historically, there have been three industrial revolutions that have characterized the Western world, to which the fourth industrial revolution has recently been added, characterized by a change in technological and cultural paradigms of such scope as to involve the manufacturing system in all its forms. Industry 4.0 derives precisely from this digital transformation that is increasingly synonymous with disruption. Before this last step, the most widespread technologies have undergone a natural evolution since the first industrial revolution until today.
- Industry 1.0: the first industrial revolution was characterized by the birth of the steam engine and the mechanization of production capable of giving greater speed and power.
- Industry 2.0: again, the main innovations have been related to energy, thanks to the use of electricity and oil. In addition, a new way of producing with the assembly line and mass production began to spread.
- Industry 3.0: a phase marked by the expansion of the fields of information technology and electronics, with the introduction of ICT and the increase in levels of automation both in production and organization. Progressive digitisation has made people’s work easier and improved its quality.
- Industry 4.0: new increasingly automated and connected production models are taking hold.
Enabling technologies of Industry 4.0
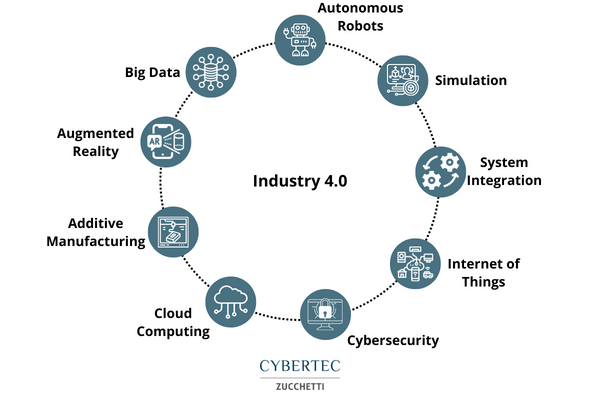
The enabling technologies that conventionally characterise Industry 4.0 are:
- Advanced robotics: interconnected machines, remotely controllable and equipped with artificial intelligence that makes them autonomous and able to support the human workforce as an integrated work unit.
The task of these intelligent machines is also to carry out the simplest and most repetitive jobs. - Additive manufacturing: 3D printing and digital manufacturing open the door to the possibility of creating customised products with complex shapes, with considerable savings on the use of raw materials and on the time taken to create prototypes or variants.
- Augmented reality: the evolution of virtual reality that integrates reality with different types of information in real time. The goal is to simplify user activity by making work even more flexible.
- Horizontal/vertical integration: all steps of the value chain communicate with each other thanks to interconnected technologies, saving time and costs throughout the production process.
- Simulation: possibility of simulating new processes related to the production activity before putting them into practice in reality, thus reducing set up times and increasing the quality of the final product because it is possible to correct the production process before starting it.
- Industrial IoT: intelligent objects connected to the Internet that allow a real-time dialogue between customers, suppliers and manufacturers.
- Cloud: management of large amounts of data directly on the network.
- Cybersecurity: network operations and cloud systems secured by standardized protocols that guarantee the confidentiality of information relevant to the company.
- Big Data and Analytics: analysis of a wide range of data to produce useful information in real time to optimise products and production processes.
The advantages of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 brings with it benefits that affect the entire company, from greater productivity to a better experience for customers. In particular:
Greater productivity: new technologies allow you to do more with less, thus producing more and faster, using resources more efficiently and with less waste, thanks to real-time production monitoring that also reduces set-up times, errors and machine downtime.
Greater flexibility due to the production of small batches that makes it easier to increase or decrease production, or introduce new products. Simplicity in making changes makes the product more competitive.
Greater sharing of knowledge and work made more collaborative: production lines, business processes and departments can communicate by spreading knowledge automatically, from machine to machine and from system to system. The interconnection between all assets (people, things and systems) makes information available to be consulted at any time. It thus provides added value in terms of cost reduction and resource availability.
Better customer service and improved customer experience: thanks to fewer problems with product availability, better quality and more choice for customers.
The risks of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 technologies are growing fast and helping companies to be smarter and more efficient. However, starting to use new digital tools is not always easy and you may encounter difficulties. The five most common barriers to entry are:
Lack of capacity to manage the complex structures typical of Industry 4.0: in particular, difficulties in finding and training personnel in various areas such as user interface, data science and software development. Difficulty in accessing technology can also result from people unwilling to use new digital tools and applications.
Cyber security concerns: Online integration between processes, systems, and people can lead to security breaches and data leaks. The risk is not only related to cyber attacks, but also to incorrect configurations and malfunctions of software or devices that can interrupt operations and production.
Other spending priorities: Equipping yourself with the technology to make your company smart can be expensive, but you don’t always have to start with a big investment. For example, you can opt for a scalable solution.
Software for Industry 4.0
The scope of production planning and scheduling can certainly benefit from all the advantages introduced by Industry 4.0. In fact, in this sector, elements such as data accuracy, the possibility of having information in real time and under the continuous control of operations personnel, as well as flexibility to adapt to uncertain market situations are characteristics that play in favor of companies.
To promote digital transformation and seize the opportunities of Industry 4.0, companies can evaluate the introduction of specific software. CyberPlan allows companies to innovate their Supply Chain with APS software, an Advanced Planning & Scheduling system.
