Throughout the production process, manufacturing industries face numerous challenges, including delivery delays, communication difficulties between departments, and sudden changes in demand.
In this context, the activity of production planning, also known as Production Planning, plays a crucial role, since it allows to optimize the production process, managing resources and activities in a precise and organized way.
Investing in a solid Production Planning strategy therefore becomes essential for business success. But what does it consist of and what tools to use for the success of a Production Plan?
Whatis Production Planning
Production Planning is the process through which industrial companies manage company resources (raw materials, personnel and machinery), in order to meet the expected demand for goods, based on the timing and market needs defined.
Without the development of a Production Plan, the production process could not exist.
In fact, it would lack a fundamental direction (roadmap) to establish the objectives to be achieved and the activities to be implemented in this regard.
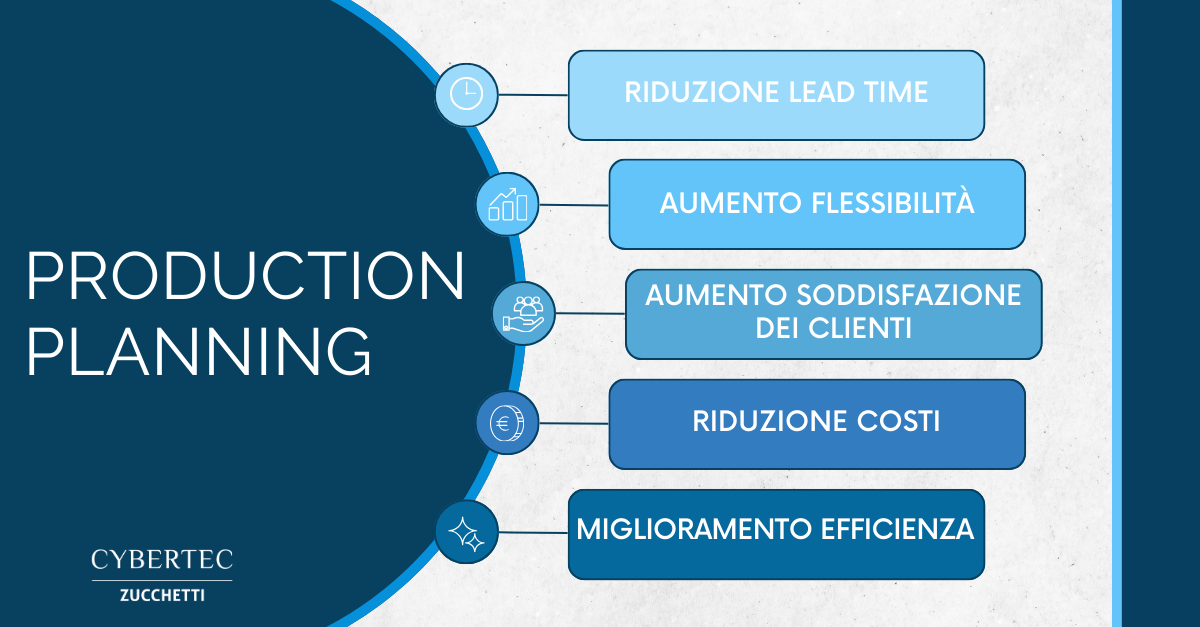
In this way, the company is able to define in advance what, how much and how to produce, generating a reduction in costs and, at the same time, an increase in production capacity.
What Production Planning is for
Production Planning is the starting point of any production operation, as it allows the company’s different departments to know in detail the orders to be made and the times to be respected.
In particular, the implementation of a Production Plan offers the following advantages:
- Reduction of waste and optimization of resources. By defining in advance the need for raw materials necessary for production, it is possible to avoid waste and organize resources through efficient management of production capacity.
- Improved efficiency. Through reasoned planning, production activities can be coordinated with a view to reducing costs and significantly improving operational efficiency.
- On-time deliveries. Planning also means optimising production times, meeting deadlines and ensuring on-time deliveries.
- Customer satisfaction. A satisfied customer is an indicator of the company’s success. A properly structured production plan ensures quality products quickly, responding to customer expectations and creating lasting relationships.
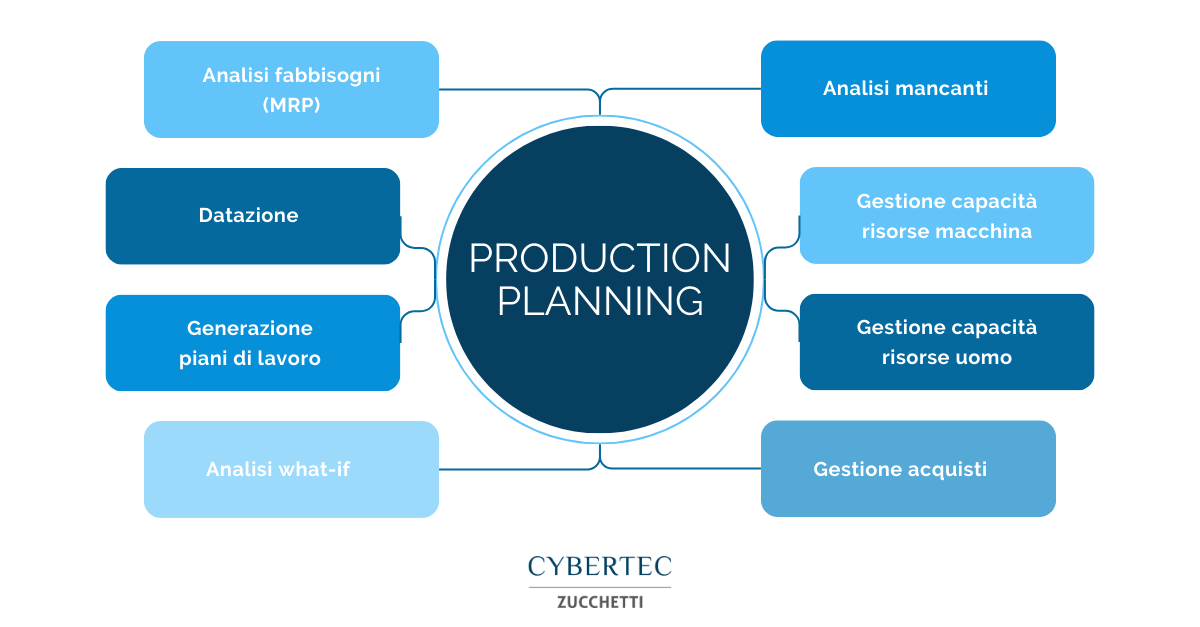
The phases of Production Planning
The Production Planning process is divided into several phases, each of which represents a fundamental step for the correct performance of production activities:
- Demand analysis. It is the first step of planning and consists of studying the needs of the market, in order to predict the production volumes needed to meet demand.
- Capacity planning. Useful resources, including materials, labor, and plant, are estimated at this stage. The goal is to determine the maximum amount of items that can be produced in a given period of time.
- Scheduling. This phase is based on the elaboration of a detailed schedule for the execution of production activities, so as to ensure that resources are allocated correctly and that the process runs smoothly.
- Monitoring and control. The last step is carried out starting from the constant supervision of production activities, so that the necessary corrections can be made in real time. This allows you to cope with sudden changes and maintain operational flexibility.
The tools of Production Planning
There are several tools that can support the Product Planning process, offering a clear and intuitive overview of the planned activities. These include:
- Gantt chart. It is a visual tool that provides an organized representation of activities as a function of time, allowing a quick understanding of the sequence and duration of operations.
This allows you to easily coordinate the different stages of production, ensuring an efficient and timely flow. - PERT diagrams. Used for managing complex projects, Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) diagrams are designed to visualize the relationships between distinct production activities, identify critical issues in the process, and assess the likelihood of completion within a given deadline.
- MRP techniques. Also called Material Requirements Planning, this methodology aims to plan the material requirements necessary for production, optimizing inventory management and ensuring that the correct quantities are available at the correct time.
- This approach avoids shortages or excess materials, improving efficiency and accuracy in supply chain management.
The Production Planner
The Production Planner is the professional who is responsible for developing and implementing the Production Plan within the production line, coordinating all activities in order to achieve operational efficiency.
The tasks of the Production Planner are different and require a thorough understanding of production operations and business dynamics.
Listed below are some of the main tasks of a Production Planner:
- Definition of objectives and strategies to be adopted
- Creation of the Production Plan
- Communication with suppliers
- Inventory management
- Coordination of resources (personnel and facilities)
- Collaboration with other departments
- Contingency management
- Data analysis and evaluation
The Product Planner must be able to balance operational efficiency with customer satisfaction, optimising production operations and ensuring that goods are available as and when required.
The ability to manage complex variables within the production chain makes the Production Planner a figure of primary importance for the company’s success in the industrial landscape.
The software for Production Planning
As planning is a long, complex and difficult to manage activity, the help of tools specialised in Production Planning (or Demand Planning) is essential to simplify processes, making them more streamlined and, at the same time, effective and incisive.
Among the options currently available, we can find:
- Spreadsheets. Obsolete solution that, although frequently used for its immediacy, presents significant critical issues in the management of industrial dynamics. In fact, spreadsheets have strong limitations in the possibility of easily governing large amounts of data, updating them automatically and making them easily usable to the other departments of the company.
- ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software. Although more advanced than spreadsheets, ERP systems can be limiting in some respects. Designed to manage company resources, these software require a specific extension for Production Planning activities. As a result, the results are unreliable and inaccurate.
- Advanced Planning & Scheduling System (APS). It is state-of-the-art software that combines sophisticated algorithms to ensure accurate and timely planning based on various factors, such as material stocks, available resources and plant capacity.
Understanding the right tools for your company can seem complicated, especially in today’s market, characterized by an increasing offer of software proposals for Production Planning.
That’s why supporting a careful analysis of the context and your business needs, together with the choice of advanced tools based on the latest technologies is essential to find the solution that best suits your production reality.
CyberPlan: the software for Production Planning
One of the most comprehensive APS software currently on the market is CyberPlan.
This tool offers advanced management of planning and scheduling processes, consistently reducing human errors, lead time and costs related to production.
If your goal is to excel in the industrial landscape, optimizing operational activities, maximizing efficiency and responding rigorously to demand demands, CyberPlan is the software solution you are looking for.
If you want to know more details, do not hesitate to contact us.
Our professionals are at your disposal for every specification and request.
REQUEST INFORMATIONHubSpot Call-to-Action Code
