A slim and light as a feather production. Lean Manufacturing, a production methodology that aims to lighten the company from a series of excess costs related to waste, could thus be described in very few words.
Lean Manufacturing was born in Japan in the post-war period and then spread to the rest of the world, bringing a new way of thinking and conceiving production to companies.
After reading this article you will know what Lean Manufacturing is, on what principles it is based, what benefits it brings and how to introduce it in your company.
Whatis Lean Manufacturing
Lean Manufacturing is a business and production management methodology that aims to eliminate what does not create value, thus aspiring to achieve total quality, according to the Kaizen philosophy of continuous improvement. The methodology aims to make the company more streamlined, in fact, relieving it of all those excess costs related to waste, overloads and changes in the production flow. It is based on two fundamental pillars:
- Just in Time, the production management system that is based on the concept of “producing only when you need to”. This makes it a “pull” system, which is activated when there is a request for the product by the customer.
- Jidoka, the search for total quality thanks to the cooperation between man and machine. According to this practice, human intervention is required at the first signal of anomaly to stop production and correct the problem so as not to reduce quality standards.
Lean Manufacturing is organized visually with Kanbans, handling or production tags. Each production centre has two storage points, one at the entrance for the materials and one at the exit for the finished product. Storage takes place in containers on which one of the two types of Kanban is applied: the handling Kanban authorises the movement of a component from one centre to another, a production Kanban is used to replace the container taken. The system requires that the containers always have the same number of components and are always stored in the same area.
The benefits of Lean Manufacturing
The main advantage of Lean Manufacturing is that it allows you to produce better using fewer resources. By minimizing waste and pursuing total quality, it also increases value creation.
The improvement extends to the entire company, because adopting a Lean production methodology requires a radical change in the company philosophy. Based on a pull system that starts from customer demand, production is proportionate to this real demand, as are activities, equipment, machinery and spaces. As a result, production becomes effective and efficient, because excess production, overwork and time spent in processes that do not bring value are eliminated.
Changes in design, production and quality management are also positively reflected in the use of people, communication and cooperation within the company.
The five principles of Lean Manufacturing
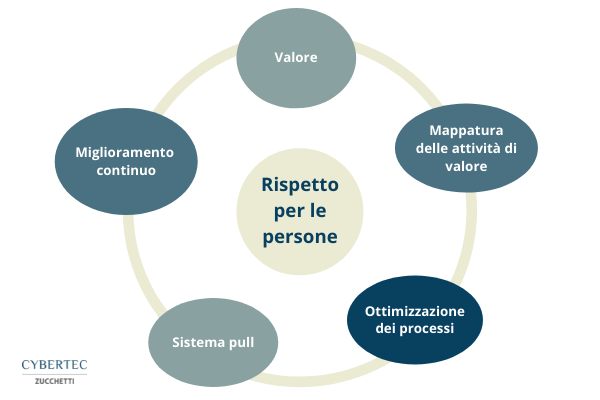
Lean Manufacturing is based on five fundamentals that, if accepted, contribute to radically changing the way the company thinks.
- Value: the concept of value must be thought of and mapped from the customer’s perspective, so as to undertake a process of correction of activities that do not contribute to its creation. It should be specified that when we talk about value, we mean what the customer is willing to pay for and for this reason it is important to know their real or latent needs. There are different qualitative and quantitative techniques to find out what customers want, how they would like the product to be delivered and the price they are willing to pay. The most common are interviews, surveys, demographic information, and web analytics.
- Mapping the activities that create value: starting from the value for the customer as a point of reference, all the activities that contribute to its creation can be identified. In this process, two types of waste will also be identified: activities without added value but necessary (to be reduced as much as possible) and activities without value and not necessary (to be eliminated).
- Optimise value-creating processes: The next step is to maximise value-creating activities, making them a continuous flow to ensure the process runs smoothly. To do this, it may be necessary to review the organization of work, what equipment to use to facilitate production, or redesign the production layout.
- Pull system: production is started only when there is a request from the customer, since it is the customer who “pulls” the production, exactly what the customer wants is produced with the certainty of selling. This allows you to lower the level of inventory and limit inventory, considered one of the greatest wastes in production, ensuring that materials are still available for a regular workflow. As a result, liquidity increases and all business management improves.
- Improvement: once the four previous steps aimed at reducing waste have been completed, a production improvement process can be initiated to achieve perfection according to the Kaizen philosophy. In this step, lean thinking and continuous improvement of processes become part of the organizational culture.
Who invented Lean Manufacturing
The birth of Lean Manufacturing is traced back to the 1950s, to the Japanese Toyota Motor Corporation. The post-war period was a period of deep crisis for Japan, which was unable to keep up with the systems of mass production that had spread with Fordism.
The need to do more with less and therefore to reduce costs while maintaining high productivity led to the birth of a new, more flexible industrial production model. Toyota established itself in the automotive industry of the time thanks to the Toyota Production System (TPS), an innovative methodology for those years, focused on the continuous reduction of waste and simplification of processes to create more added value for the end customer, who dictates the pace of production.
As for the term “Lean Production”, its first appearance dates back to 1988, when it appeared on an article coined by a former Toyota engineer. But it only became more widespread after the publication in 1990 of a book that studied the future of the automotive industry by analyzing the Toyota production system and associating it with Lean Production.
Software for Lean Manufacturing
By introducing the logic of Lean Manufacturing in your company, you can obtain great advantages from the point of view of added value, competitiveness and flexibility, all important requirements to successfully dominate a market that continues to evolve.
The first step in undertaking this journey is to choose a software solution to manage production planning effectively, optimizing inventory and reducing waste.
CyberPlan Demand Driven is the solution dedicated to those who aspire to manage production planning by reducing forecast errors and reducing variability. Download the brochure to see all the features.