For some time now, people have been talking about a new industrial era. Here’s what Industry 5.0 is and what impact it will have on industry and workers.
Whatis Industry 5.0
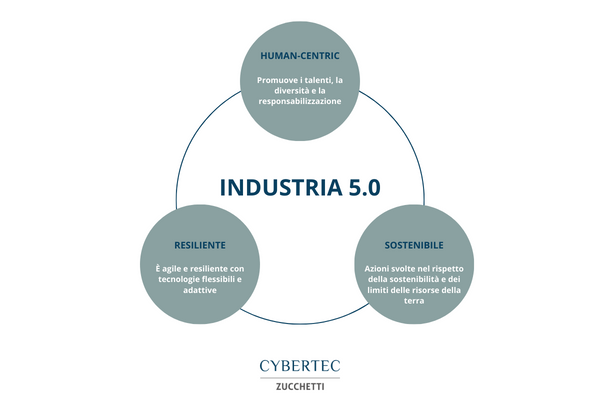
The European Union has defined Industry 5.0 with three words: sustainable, with man at the centre and resilient. Precisely thanks to these defining concepts, the new industrial era will bring with it benefits for both workers and companies. In fact, the focus will shift to the well-being of the worker, placed at the center of the production process thanks to the use of new technologies that will aim to keep the company competitive while respecting the limits of the planet’s resources, giving rise to a new model of industry that embraces the ecological transaction.
Industry 5.0 is the natural evolution of the previous Industry 4.0, as it continues to exploit the advanced technologies typical of the previous phase, namely the Internet of Things, big data and artificial intelligence, combining them with man’s creative potential to promote a greater balance between human beings and increasingly intelligent technologies. Technology, therefore, is used to adapt production and make it more in line with the needs of the worker, including respect for his fundamental rights such as privacy, autonomy and dignity.
The advantages of Industry 5.0
The long-term benefits of adopting Industry 5.0 reflect its core values. For example, better talent attraction and retention, greater energy savings, and greater overall resilience. Advantages that contribute to improving the competitiveness of companies, which can successfully adapt to a changing world and new markets.
Increased efficiency
Industry 5.0 technologies provide companies that adopt them with the tools to be able to react to sudden changes that may occur in the supply chain, managing to maintain an efficient management of activities.
Customization
The combined use of advanced technology and human inputs allows us to expand the potential for customisation of goods. Machines perform the repetitive tasks, while humans oversee the process and ensure that all requests are fulfilled. Technology is used to collect data and analyze customer inputs by providing insights for manufacturers, better understanding customer preferences. Then sensors and tools intervene to make the personalization experience accessible.
Cost reduction and sustainability
Sustainability is another benefit of Industry 5.0. As mentioned, this is one of the concepts underlying the new industrial era, but it also brings with it long-term advantages related to competitiveness. Attention to sustainability is a relevant issue for a growing number of stakeholders, therefore paying attention to these issues will make the company more attractive to investors, but also employees and consumers.
Increased quality
In recent years there has been a lot of talk about the phenomenon of large resignations, a phenomenon for which many employees have resigned to prefer better well-being. It is increasingly difficult for companies to attract and retain skilled and talented employees, who base their choices on their personal well-being and are less tied to the companies they work for. This is even more true when the tasks performed are repetitive and related to operations to be performed mechanically on the machines. Industry 5.0 instead creates a more stimulating work environment, where people’s creative input is needed and, as a result, greater employee satisfaction and loyalty is also created. In addition, the focus on sustainability can make the company more attractive in the eyes of an employee related to these issues.
Improved safety
Another advantage is to make the factory environment safer. This is possible thanks to technological machinery that performs the most strenuous and dangerous functions in place of men. According to Eurostat data, the top three sectors in which workplace accidents occur are those where hazardous and strenuous tasks could be easily automated.
The components of Industry 5.0
The technologies of Industry 5.0 follow those of the previous phase, adding new practices to them with the aim of putting people at the centre and creating a more fluid interaction between humans and machines.
Automation
The use of technology and the digitization of the factory allow the automation of simple and repetitive tasks, easy to standardize, but also of the most tiring or dangerous ones.
Interconnection
The integration between the machines and the collaboration between man and robot allow to obtain a large amount of data and to know better the production processes. The use of integrated sensors, actuators and machine learning technologies facilitate interconnection and the information collected contributes to reducing waste, increasing the drive for sustainability and using resources more efficiently.
Big data
Data is becoming more and more numerous, knowing how to analyse and synthesise it into useful information is as difficult as it is important. Leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning, advanced data management and analysis systems built on the needs of individual companies reduce waste and inefficiency.
Simulation and virtual reality
Simulation models simplify worker learning and efficiency, enabling innovation and creativity with minimal operational risk.
The challenges of Industry 5.0
As difficult as it is to find disadvantages in Industry 5.0, the main challenges for companies lie in how organizations will manage to approach this new paradigm overcoming initial barriers to entry.
High initial costs
The adoption of new technologies always requires time and effort, as well as an initial economic investment for the purchase and introduction of new technologies in the company that may not be sustainable for start-ups or small and medium-sized enterprises.
Cybersecurity
Workers will have to develop new skills to learn how to collaborate with intelligent machines, both from a soft skills and technical skills point of view. The need to program industrial robots and manage them will create new jobs for data analysts, integrators and cybersecurity experts.
Training and qualifications of workers
To make the most of digital innovation, new technologies plan to connect more and more devices through IT systems. But the more this interconnected system expands, the more possible entry points for cyberattacks open up, posing a new cybersecurity challenge.
Industry 5.0 Human Centric
The most distinctive element of Industry 5.0 is the central role given to man, at the centre both because greater importance is given to his well-being, and because the worker takes on a prominent role within production.
Work is increasingly considered as one of the factors that contribute to a person’s personal fulfilment, consequently values and company culture have an important weight in the choice of workplace and at the same time companies strive to make themselves attractive in the eyes of potential employees, paying attention to their well-being.
But the centrality of man is not limited to this. As part of increasingly automated production processes, humans have the important task of influencing processes by contributing with their creativity. Industry 5.0 technology does not transform production into a simple automated process, where machines perform the tasks for which they have been programmed. On the contrary, the new industrial era introduces collaborative robots (called cobots) in factories, which operate in synchrony with employees, complementing each other.
On the one hand, machines perform repetitive operations, but also those that are tiring or dangerous, while workers use their creativity to engage in more complex and responsible activities. According to this Industry 5.0 paradigm, technology does not take away jobs, but makes jobs safer and contributes to improving employee satisfaction and well-being.
Industry 5.0 and Industry 4.0: differences and similarities
Industry 5.0 originates from the previous phase of Industry 4.0. With this, it shares the strong digitization of processes through the use of advanced technologies, but it does not stand out as a further technological revolution, but rather represents a cultural revolution.
Industry 4.0 has been defined as the fourth industrial revolution because it has profoundly changed the structure of factories and processes by introducing new technology and reshaping the industrial paradigm on the concepts of enabling technology, efficiency and productivity. A revolution focused much on means and tools, but less on people, their role and the development of sustainable models for society and the environment.
Industry 5.0 fills this gap by imposing itself as a cultural revolution, which puts people, the environment, quality of life and sustainability at the centre of the production process, while exploiting the support of typical Industry 4.0 technologies.
Software for Industry 5.0
Putting technology at the service of human well-being is the philosophy on which Industry 5.0 is based. Inspired by a completely similar value, CyberPlan was born more than 30 years ago, with the aim of putting technology at the service of the supply chain and those who work in the supply chain.
CyberPlan is the Advanced Planning and Scheduling software developed with the best technologies to make it possible to simplify complex decisions and enhance human capacity in the production planning process. In particular:
- Make it easy and intuitive for managers to make decisions in order to enable them to respond to rapid changes in the market;
- Thanks to an intuitive interface, be suitable for everyday use, improving the end user experience;
- Generate value for the company, linking operations with business objectives.
