Those from a manufacturing company will most likely have heard about ERP and MES systems and how they can help the company perform better. These are two complementary solutions but very different from each other, with different areas of expertise and ways of operating.
It is understandable to ask yourself which software to choose and which solution to prefer, even if the best choice is to adopt both solutions. That is why.
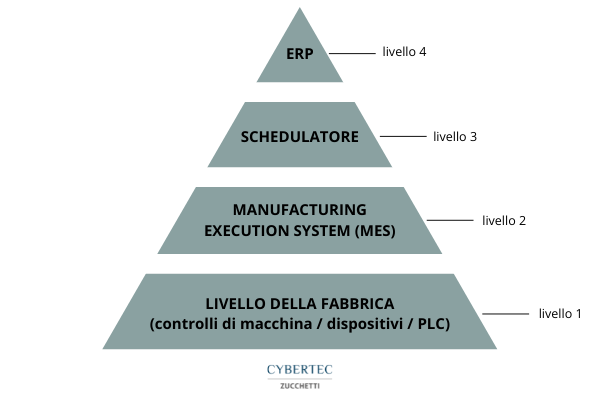
Whatis an ERP
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a management software useful for managing the commercial aspects of production. ERPs collect and centralize information from various company departments and related to the activities carried out, allowing resource planning and control of the work done.
Specifically, it manages and controls data relating to orders, purchases, sales, warehouse, inventory, allowing the various company departments to be aligned with the creation of a single database used to integrate and interact the different business processes. ERP is among the most used software by companies around the world and by monitoring the company’s performance it is a valuable ally, especially for the administrative department and management, as it provides tools and procedures for making strategic decisions.
Whatis a MES system
The MES (Manufacturing Execution System) monitors aspects related to production functions, such as activities carried out, personnel involved, machinery used, production times… a whole series of data collected in real time and fundamental to make the product as required. Carries out an operational function in the field of production, managing, controlling and optimising operations related to the production process.
The MES system has the valuable task of aligning management and production, connecting and communicating all company systems and ensuring consistency between what is planned and the actual state of the processes.
What are the differences between ERP and MES?
ERP and MES software differ mainly in three areas.
First of all, they have different functions, deriving from the different roles they play within the production plants. The ERP system is focused on planning and quantitative analysis aspects, while the MES system monitors the production line and the operations that take place in the shop floor in real time.
The way in which data is acquired and delivered is also different. As can be understood, in the case of the MES, the reports are made available in real time, while an ERP system produces general reports over a certain period of time, which can be hours, days, months or years.
Finally, the way they are integrated also changes between the two systems. For the MES system, the integration takes place directly in the machinery present in the factory, and this allows the instantaneous collection and delivery of data. Instead, an ERP software is integrated with other business tools such as CRM.
Why integrate ERP and MES?
Integrating the ERP and MES systems means maximising efficiency and production agility by putting two complementary realities in communication: on the one hand, the directional one represented by the ERP and on the other, the productive one represented by the MES. This is because the integration between production and business leads to an alignment between factory activities and demand, allowing lead times to be reduced and production times to be respected. In addition, more accurate demand forecasts can be obtained, avoiding stock outbreaks or production beyond what is necessary. The visibility on the data allowed by the integration between ERP and MES also allows to analyze in depth the costs, both direct and indirect, and to carry out preventive maintenance.
Integration is essential because the MES is critical to providing real and accurate data and enabling the ERP to support planners and likewise the MES needs to communicate with offices to align factory activities to demand. To understand this, you can refer to an example case. Thanks to the ERP, the administration can plan in advance the orders of raw materials for production, reducing delays and the level of stocks. The MES, on the other hand, collects real-time data on the materials used by the machines and manages any problems on the machine. Working together, the two systems ensure more efficient operations and faster decisions.
The disadvantages of integration between ERP and MES
For most companies, especially small ones with a limited budget, the main limitation in the adoption of ERP and MES systems is given by a cost in some cases prohibitive, both of the software itself and of the subsequent implementation and maintenance. While the cost of software is one of the most important factors to consider when purchasing, small businesses can often avoid much of the upfront costs by choosing a cloud solution. With regard to implementation and maintenance, account should be taken of the time required for these processes, which may require additional IT staff or external consultants.
Added to this is what can be seen as another obstacle, namely the complexity of software of this type. The many features present can make the solutions difficult to understand and use and consequently, despite the initial investment, the systems are not properly implemented.
The software for the integration between ERP and MES
The potential of ERP and MES systems can be exploited even more with the implementation of an additional system, which at the structure and function level lies between the two. These are APS solutions, which process data from ERP and MES to make optimised production plans available to the company.
Cybertec offers a unique and extremely innovative APS solution, able to dialogue with the ERP and MES systems present in the company. CyberPlan has a minimal impact on corporate information systems, an impact completely balanced by obtaining business results above expectations, especially with regard to increasing punctuality, reducing inventories and increasing the efficiency of departments.
Among the most well-known and valid MES on the market is Opera MES by Open Data, a company founded in 1994 to create the first online information systems for the management of the factory and today among the main players in the market. Opera is a MES (Manufacturing Execution System) platform used by manufacturing companies to create the Connected Factory, thanks to the power of information, made possible by digitisation, data acquisition and integration, the interconnection of resources and processes, AI and Predictive Analytics.
To learn more about CyberPlan’s advanced planning and scheduling solution and the techniques used for integration with ERPs and MES systems, contact an expert who can answer all your questions.
