In this article we analyze a very articulated process carried out in manufacturing companies, which aims to ensure that only what is needed is produced, in the appropriate quantities and times and at the lowest possible cost; a clear but far from trivial goal to be achieved. Let’s find out what is meant by Master Production Schedule.
Whatis the Master Production Schedule
The Master Production Schedule, also known as MPs or main (aggregated) production plan, is a general production plan useful for evaluating the production of individual finished products. It aims to translate the demand for finished products into production capacity requirements and compare them with the available production capacity. This is not so obvious since the production lines are dedicated to the production of various items and also compatibility for the various types of products is not discounted, in terms of time. The MPs defines the production plan to illustrate the duration of each phase to produce each final item, also specifying how much must be produced within a certain period. In essence, the main production planning is the backbone of a production company, and serves to:
- Make changes to demand fluctuations;
- Prevent inventory;
- Improve production efficiency;
- Carry out effective cost control.
In this article we will look at MPs and how it is used in production.
What the Master Production Schedule is for
The purpose of a Master Production Schedule is mainly to make the management of the production flow much more efficient and therefore to save time. Once you understand the ultimate goal of MPs, you can understand that the other goals of MPs are aligned in achieving this goal. The other functions of an MPs are:
Understanding production plans
How will you manage operations to find a balance between demand and production capacity, both in terms of personnel and equipment? The Master Production Schedule will help you determine how many products you will need to make in a given period of time, to meet customer orders on time and maintain a great level of service.
Evaluate alternative scenarios
A Master Production Schedule should consider multiple production plans to discover the most efficient one and take into account any problems that may arise along the production line.
Generate production capacity requirements
Generating capacity plans (also known as rough-cut capacity planning) with MPs helps you determine the capacity you’ll need to meet demand, increase profits, and minimize costs.
Facilitate information analysis
MPs helps you set reorder points for deliveries that need to be requested. You can do this by coordinating different information management systems such as marketing, accounting and others.
Resource utilization
Finally, an MPs schedule helps you establish needs in terms of loads and use of resources and machinery.
Additional objectives of the MPs plan are:
- Make the flow of demand more regular and predictable;
- Keep the lead time low;
- Uniform internal communication;
- Helping to prioritise purchase orders;
- Helping to keep production levels stable;
- Generate feasible production plans for production orders;
- Support the creation of purchase orders.
These are the desired outputs of the MPs plan.
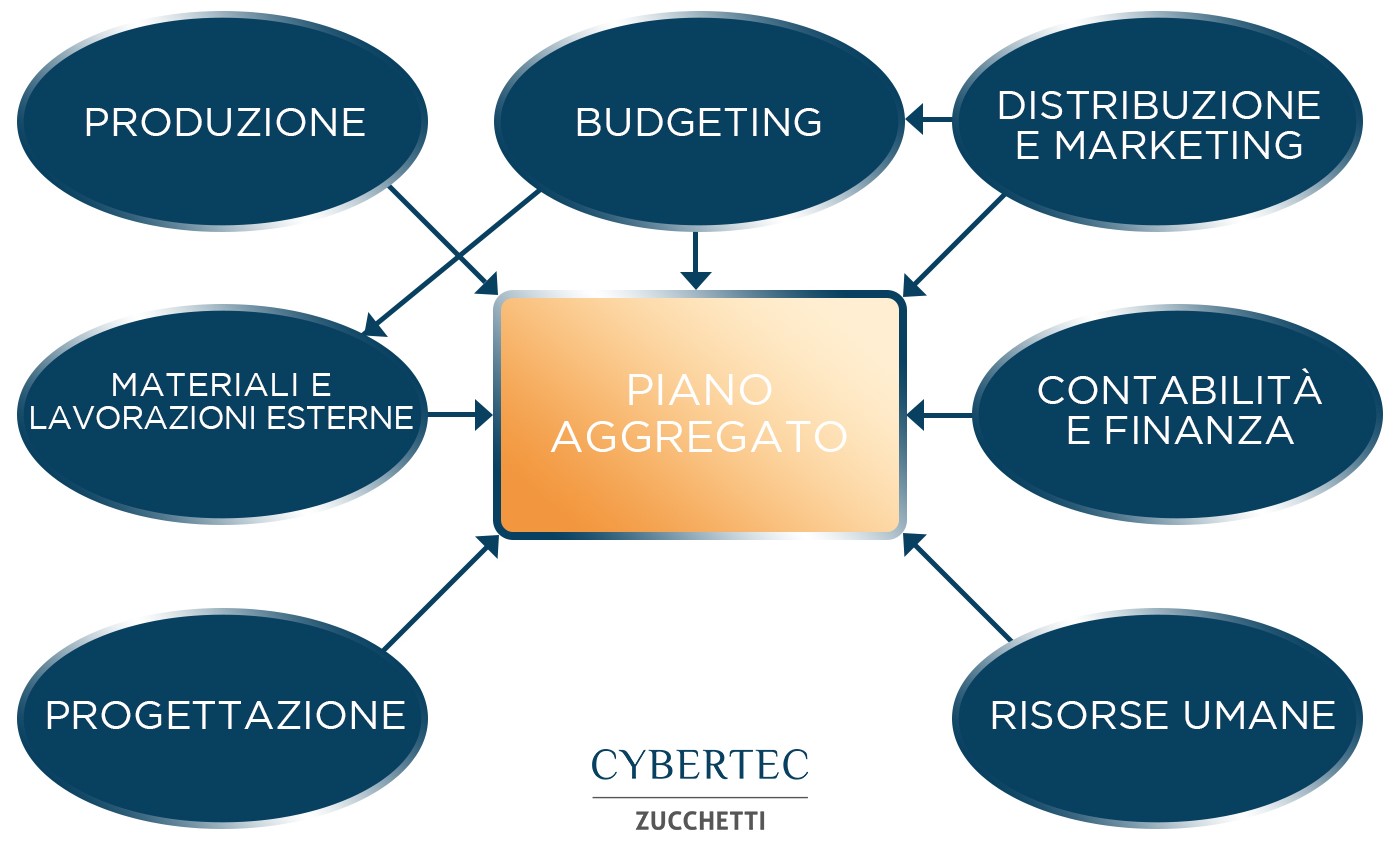
The benefits of the Master Production Schedule
There are many advantages for a manufacturing company in introducing an MPs. These include:
- Provide a solid basis for building, monitoring and improving sales forecasts;
- Provide a solid basis for calculating the quantities of components, parts or raw materials to be purchased or produced, as part of the next phase of MRP planning;
- Provide a solid basis for calculating desired inventory levels;
- Provide a solid basis for calculating the required amount of manpower and shifts, as part of the next phase of MRP planning;
- Allow to optimize the installed capacity and balance the load of the system;
- Production may include the production and maintenance costs associated with the work centres;
- The company’s finance department can obtain revenue and expenses, which come from the MPs, and produce forecasts of the company‘s cash flows. MPs helps create other financial statements, such as balance sheets, income statements, loss statements, and investment plans.
- The human resources department can use MPs to forecast labor requirements and hiring.
- Minimize costs/maximize profits;
- Maximize the level of service to customers;
- Minimize the cost of inventory management (MRP);
- Balance the workload deriving from production over time;
- Minimize changes in the workforce;
- Maximise the use of plant and equipment.
The MPs must be able to reflect the business plan as accurately as possible; to do this, it must be updated in a timely manner with everything that happens in the company. For example, it must take into account possible actions of the Marketing and Sales department that could have effects on sales orders.
In addition, the MPs is a useful resource to discuss and confirm the plan with the planning department, to plan promotional campaigns and to achieve a high level of collaboration between the different departments of the company.
Finally, the MPs lays the foundation for the formulation of the Material Requirements Plan (MRP). MRP planning offers a higher level of detail, both in the division of items and in the analysis of timing, it should be borne in mind that MRP divides each item into individual components.
An example of a Master Production Schedule
Let’s see an example of a Master Production Schedule for a company that produces leather bags. For simplicity we will assume that you create two bags, one in two colour variants and one in three colour variants, for a total of five total SKUs. Assuming that the company has the information regarding the available inventory and the expected demand, the production quantity is calculated based on the current inventories, demand and production capacity. Let’s see what all this looks like in a basic production schedule.
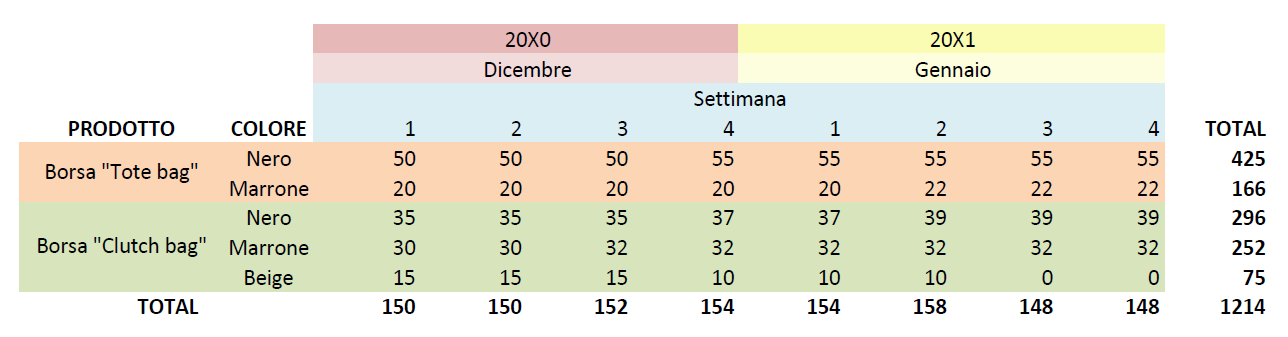
The image above shows an example of a Master Production Schedule still used by some companies. Although it contains several pieces of information, such a spreadsheet can be difficult to read, difficult to update and often leads to error; a further negative aspect of this approach is that an MPs is not dynamic. In fact, it does not change based on current orders and capacity. The operator must update it himself since it is based on spreadsheets that are inefficient, isolate the information and do not update without the intervention of an operator.
Differences between MPs and Production Scheduling
“Master Planning” is a term that derives from the optimization process, in the sense that the quantities to be produced of each unit are defined according to the constraints and inputs. The final product of Master Planning efforts is the overall production plan or (Master Plan). This plan is not static but should be renewed weekly or monthly. MPs involves planning and is much more complex than scheduling.
Scheduling answers the “when” question by setting a timeline that lists things to do in chronological order. An example of scheduling is when someone schedules their own appointments at the dentist, including the list of tasks using a calendar, and sometimes determines who will take responsibility.
Unlike planning, MPs involves planning activities across many categories, resources, departments, and people. These categories can be further broken down into higher levels of detail for distribution to multiple team members. Finally, the team members involved coordinate and work simultaneously to achieve a common business goal. On the other hand, MPs is not the same as production planning. Production scheduling is the stage before MPs and defines production levels at higher levels and with less detail. Production planning establishes the amount of production in terms of households rather than individual items.
Taking a concrete example about a chair production company, the production planning defines how many chairs should be produced, while the MPs will take into account the individual Stock Keeping Units (SKUs). In the case of production planning, the planning horizon is also the medium term, from 6 months to 24 months. Production planning assists in determining required resources, formulating inventory levels at higher levels, and is a practical plan for top management to view activity from a production perspective.
The software to implement MPs
Today, manufacturing companies can enjoy the competitive advantage offered by production planning and scheduling software to achieve an up-to-date, accurate and effective MPs. These software integrate perfectly with management systems (such as Zucchetti, Oracle and SAP), dialoguing with them and exchanging accurate, timely and up-to-date data. Find out what CyberPlan users are saying or contact a Supply Chain expert, express your doubts and get the best advice from a company with over thirtyyears of experience, part of the largest Italian group in the sector.

